本文最后更新于:June 20, 2022 pm
单调栈模板
栈是一种简单的先进后出的数据结构,单调栈实际上就是栈,只是利用了一些逻辑,使得每次新元素入栈后,栈内元素都保持有序。单调栈的用途不太广泛,只处理一种典型的问题,叫做Next Greater Element。
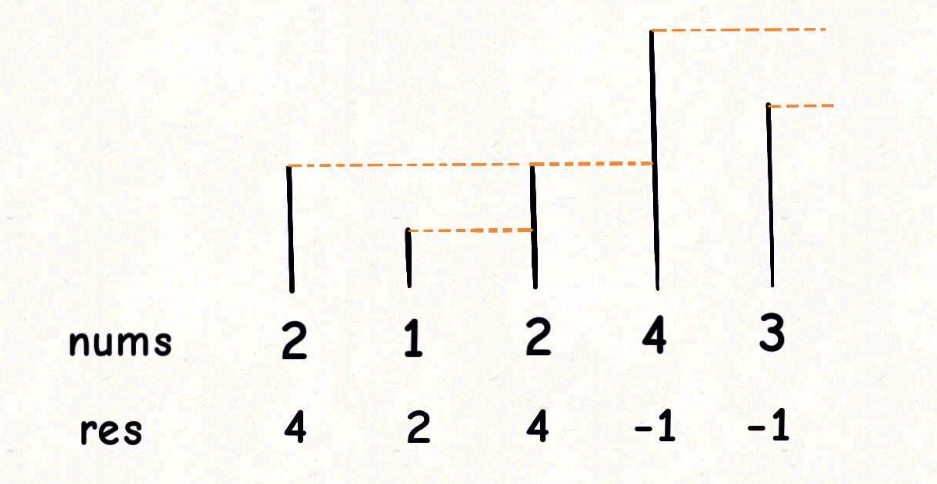
题目如下:提供数组nums,请返回一个等长的结果数组,结果数组种对应索引存储着下一个更大元素,如果没有更大的元素,就存-1。
| int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums) {
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() <= nums[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
res[i] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
stack.push(nums[i]);
}
return res;
}
|
以上就是单调队列解决问题的模板。for 循环要从后往前扫描元素,因为借助的是栈的结构,倒着入栈,就是正着出栈。while 循环是把两个 个子高 的元素排除,因为他们的存在没有意义,前面挡着个更高的元素,所以不可能作为后续进来的元素的Next Great Number了。
这个算法的时间复杂度其实是O(n),从整体来看:总共有 n 个元素,每个元素都被 push 入栈了一次,而最多会被 pop 一次,没有任何冗余操作。所以总的计算规模是和元素规模 n 成正比的,也就是 O(n) 的复杂度。
LeetCode496题-下一个更大元素 I
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n = nums1.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = nums2.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() <= nums2[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
map.put(nums2[i], stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek());
stack.push(nums2[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = map.get(nums1[i]);
}
return res;
}
|
问题变形
LeetCode739题-每日温度
相同的思路,直接使用模板稍作改动。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n = nums1.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = nums2.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() <= nums2[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
map.put(nums2[i], stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek());
stack.push(nums2[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = map.get(nums1[i]);
}
return res;
}
|
处理循环数组
LeetCode503题-下一个更大元素 II
一般通过%运算符取模,来获得环形特效。对于这种需求,常用套路就是将数组长度翻倍。
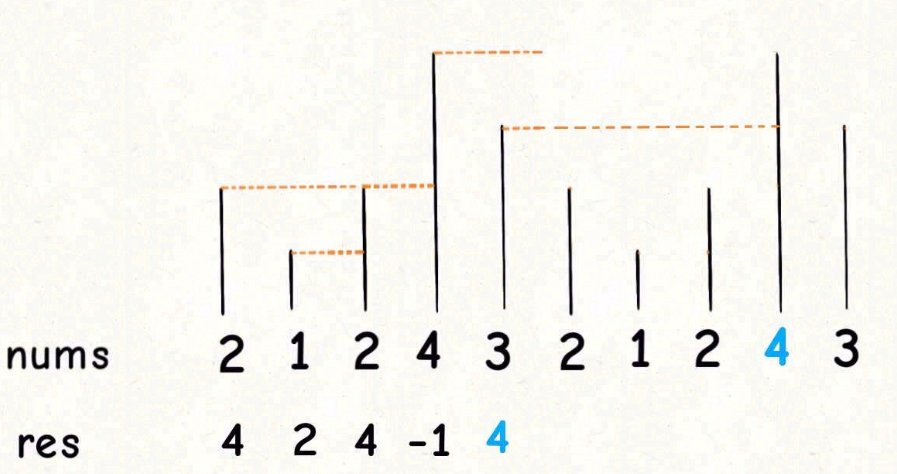
思路就是把这个双倍长度的数组构造出来,然后套用算法模板。但是,我们可以不用构造新数组,而是利用循环数组的技巧来模拟数组长度翻倍的效果。
| public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int n = nums.length;
int[] answer = new int[n];
for (int i = 2 * n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() <= nums[i % n]) {
stack.pop();
}
answer[i % n] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
stack.push(nums[i % n]);
}
return answer;
}
|




